

They both are the two types of spatial data in GIS. If the image becomes blurred or pixelated, its most likely a raster file. The entire area of the map is subdivided into a grid of tiny cells, or pixels. Whereas, the raster data represents a grid matrix. Raster data can be thought of as being similar to a digital photograph. The vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices as points, lines and polygons. Hence, there are some primary difference between Vector and Raster data. Example- Temperature, air pressure, elevation, flow and distance etc.įigure 1 Vector and Raster data representation Conclusion Example- Administrative borders, roadways, rivers, location of a house, forest area, fallow land etc.Ĥ. It consists of cells organised in rows and columns with each cell having one value.Ĥ. It is used to store data having discrete boundaries in Point, Line and Polygonġ.
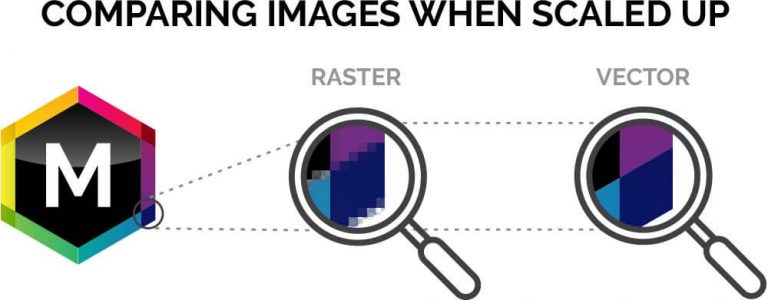
(see figure 1) Difference Between Vector Data and Raster Data Vector Dataġ. Hence, a number of raster layers are required for the representation of multiple features over a common plane. Pixels represent each and every geographic element. Raster data is synonyms with grid data as it consists of pixels with an array of cells. Examples- Forest area, Agricultural land, snow cover etc. Polygon feature is mostly distinguished using thematic symbols or colours for visual representation. It takes a minimum of three pairs of coordinates, i.e., X1Y1, X2Y2, X3Y3 to represent an area or polygon. uses discrete elements such as points, lines, and polygons to represent the geography of real world entities Raster data model. The raster data are made of pixels or grid calls and can be. Vector maps are two-dimensional maps that use geometrical shapes such as points, lines, and polygons to represent geographical features. Polygon Data– Polygon data is represented as a closed line encompassing an area. The vector data can be stored in shapefiles, databases or various others GIS file formats. This process is widely used for data input (digital scanning of vector maps) and somewhat less widely used for data conversion (output of GIS data to specific.For example rivers, railway lines, roadways etc. The start and endpoints are called nodes and the points on curves are called vertices. Line Data– It is used to represent the data that have linear features which contain at least two pairs of coordinates such as X1 Y1, X2 Y2.For example, the location of a house, location of a well etc. It is most commonly used to represent non-adjacent features and discrete data points.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
